As the Protective Outer Layer, the Jacket is an Essential Part of the Electrical Cable
Similar to the coats and jackets we wear on cold winter days, the main reason for the jackets, or sheaths, on electrical cables is protection. While a cable jacket also offers aesthetic features such as color and labeling customization, its ultimate purpose is to protect the materials inside, especially the conductors and insulation, from outside threats. At the same time, it also helps protect people and the surrounding environment from the electrical current inside.
Water, chemicals, extreme temperatures, mechanical stress, and surrounding electromagnetic energy can cause a cable to be compromised leading to poor performance or complete failure of the system for which the cable is supplying power or data. While cable sheathing has little to do with the cable’s electrical performance, it is the first and most significant line of defense against threats, hence why it is typically made of extremely durable material best suited for its intended use.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Cable Jacket
There are several key factors that go into selecting jacket material with the right properties to ensure optimal safety, performance, and longevity in the cable’s future environment and application.
During the design process, a cable manufacturer has to determine if the cable will need:
-
- Water/moisture resistance
- Chemical resistance
- Abrasion resistance
- Oxidation resistance
- Fire retardancy
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation protection
- Ability to withstand temperature extremes & fluctuations
- Electrical insulation capability
- Dielectric strength
- Flexibility
- Tensile strength
- Compliance with safety regulations & industry standards
Not sure about which cable jacket is right for your specific application? Contact CAI today and our expert team of designers and engineers will help ensure your cables are designed and manufactured.
Common Types of Cable Sheathing
There are several different types of cable jacket materials available, each with their own distinct properties, advantages, and disadvantages. Understanding the characteristics of these sheathing materials and what they offer is essential to choosing the right one. Material mixtures as well as added fillers, plasticizers, activators, and inhibitors can also be used to enhance a particular physical characteristic.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Due to its extreme versatility, cost-effectiveness, and many desirable properties, PVC is the most commonly used sheathing material, found in many of the electrical and communication cables used today. Inherently flame retardant, this thermoplastic offers good flexibility, tensile strength, easy installation, and resistance to moisture, oil, and abrasion. However, it is not suitable for extreme temperatures or UV, as it can become brittle and cracked when overexposed to sunlight for long periods, making it more suitable for indoor use.
PVC is often combined with additional additives to change its properties. For instance, to counter PVC’s release of toxic gasses when burned, Low Smoke (LS) cable sheaths combine PVC with additional additives to reduce the amount of smoke produced when the polymer is burnt. Different variations include LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) and LSF (Low Smoke & Fume).
PUR (Polyurethane)
Known for its notch-resistance and flexibility even at low temperatures, PUR is a strong, versatile polymer that can be thermoplastic or thermoset, depending on the compound used.
Possessing exceptional mechanical properties, PUR jackets are extremely durable and highly resistant to abrasion, fluids, oil, chemicals, and UV. Their great memory properties make them a popular choice for retractile cords. However, due to its limited temperature range, it’s not great for extreme temperatures as it can become rubber-like in extreme heat. PUR is also not easily recycled or as inexpensive as PVC which is why it’s typically only used in jackets for specialist applications.
PE (Polyethylene)
PE is another thermoplastic polymer which shares properties with the plastic products that permeate our society. Tougher and more rigid than PVC sheathing, PE is great for outdoor applications both above and below ground, especially when combined with additives such as ultraviolet absorbers. However, PE is harder to recycle and typically more costly to produce than PVC. Low density PE (LDPE) sheaths offer a more flexible version, high density PE (HDPE) is more durable than regular PE and often used with direct burial cables with minimal risk of degradation.
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) is one of the rare polymers that is available in both thermoplastic and thermoset forms. Exhibiting exceptional physical properties, the thermoset CPE jacket (cross-linked PE) is highly versatile and suitable for many applications. While not as strong against high-temperatures, thermoplastic CPE jackets offer excellent oxidation, heat, oil, UV, and flame resistance.
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer)
A low-density compound combining plastic and rubber, TPE offers enhanced pliability, chemical resistance, and durability. Able to withstand extreme temperatures and resist bacterial growth, TPE sheathing is popular in industrial and medical applications. One of its few weaknesses is its limited flame resistance.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene)
Ideal for applications involving extreme temperatures and corrosive environments, PTFE, aka Teflon, is a synthetic fluoropolymer with excellent thermal, chemical, and electrical resistance properties. It’s non-flammable, very flexible, non-toxic, and unaffected by most fuels, oils, and fluids. However, PTFE can be considerably more expensive than comparable options like HDPE.
Rubber
Used in cable sheathing long before synthetic polymers became the standard, natural rubber is extremely flexible and maintains its flexibility over a wide range of temperatures. It’s also highly water- and chemical-resistant. However, due to high cost, natural rubber has been largely eclipsed by synthetic rubber compounds which are much more cost-effective and even more durable.
Neoprene
One of those synthetic rubbers is neoprene, or polychloroprene, which delivers superior abrasion, cut, UV, oxidation, and chemical resistance. It also offers good tensile strength and flexibility. Extremely flame retardant and durable over a wide temperature range, it is a preferred material for demanding applications such as those found in the military and mining.
Silicone
Silicone is an extremely flexible non-carbon-based polymer that is highly resistant to extreme temperatures, UV, chemicals, and bacterial growth, making it a popular choice for food and medical applications. It also offers long storage life, good bonding properties, and no smoke or toxic gasses when burnt. Its disadvantages include its high cost to produce, average abrasion resistance, and limited recycling options.
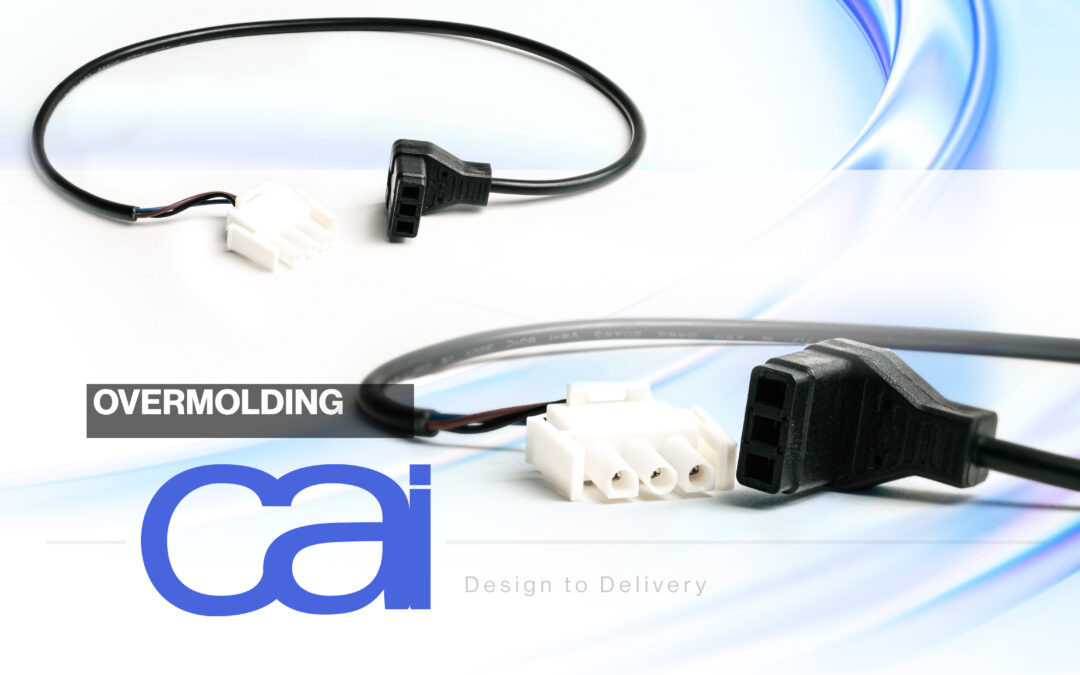
Overmolding for Superior Protection
For enhanced durability and protection, CAI combines quality off-the-shelf cable solutions with the process of overmolding which covers a cable assembly with an extra layer that seals cables and connectors into a single, stronger unit. Overmolding also offers greater overall customization, aesthetics, and organization.
With over 35 years of experience creating high-quality cable assembly and wire harness solutions, CAI will help you find the perfect jacket material for your application and installation environment. Reach out to us today to discuss your next electrical project with our experts.